概览
使用 fork 后,可能需要获取 fork 的进程的运行状况,比如有没有异常、崩溃。
wait 在 man 中关键的描述如下:
All of these system calls are used to wait for state changes in a child of the calling process, and obtain information about the child whose state has changed. A state change is considered to be: the child terminated; the child was stopped by a signal; or the child was resumed by a signal.
示例代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
int status;
printf("before fork\n");
fflush(stdout);
if ( (pid = fork()) < 0)
{
printf("fork error\n");
}
else if (pid == 0)
{
printf("after fork, child\n");
// 4种测试情况
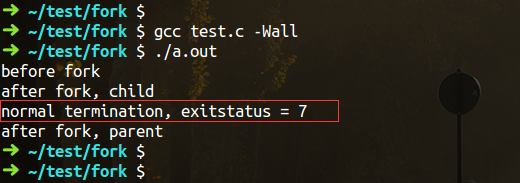
exit(7); // -> normal termination, exitstatus = 7
// abort(); // -> abnormal termination, signalstatus = 6 (SIGABRT)
// int i = 1 / 0; // -> abnormal termination, signalstatus = 8 (SIGFPE)
// char *p = NULL; *p = 'a'; // -> abnormal termination, signalstatus = 11 (SIGSEGV)
}
wait(&status);
if (WIFEXITED(status))
{
printf("normal termination, exitstatus = %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
else if (WIFSIGNALED(status))
{
printf("abnormal termination, signalstatus = %d\n", WTERMSIG(status),
#ifdef WCOREDUMP
WCOREDUMP(status)?"(core file generated)":"");
#else
"");
#endif
}
else if (WIFSTOPPED(status))
{
printf("child stopped, signal number = %d\n", WSTOPSIG(status));
}
printf("after fork, parent\n");
return 0;
}
|
运行效果